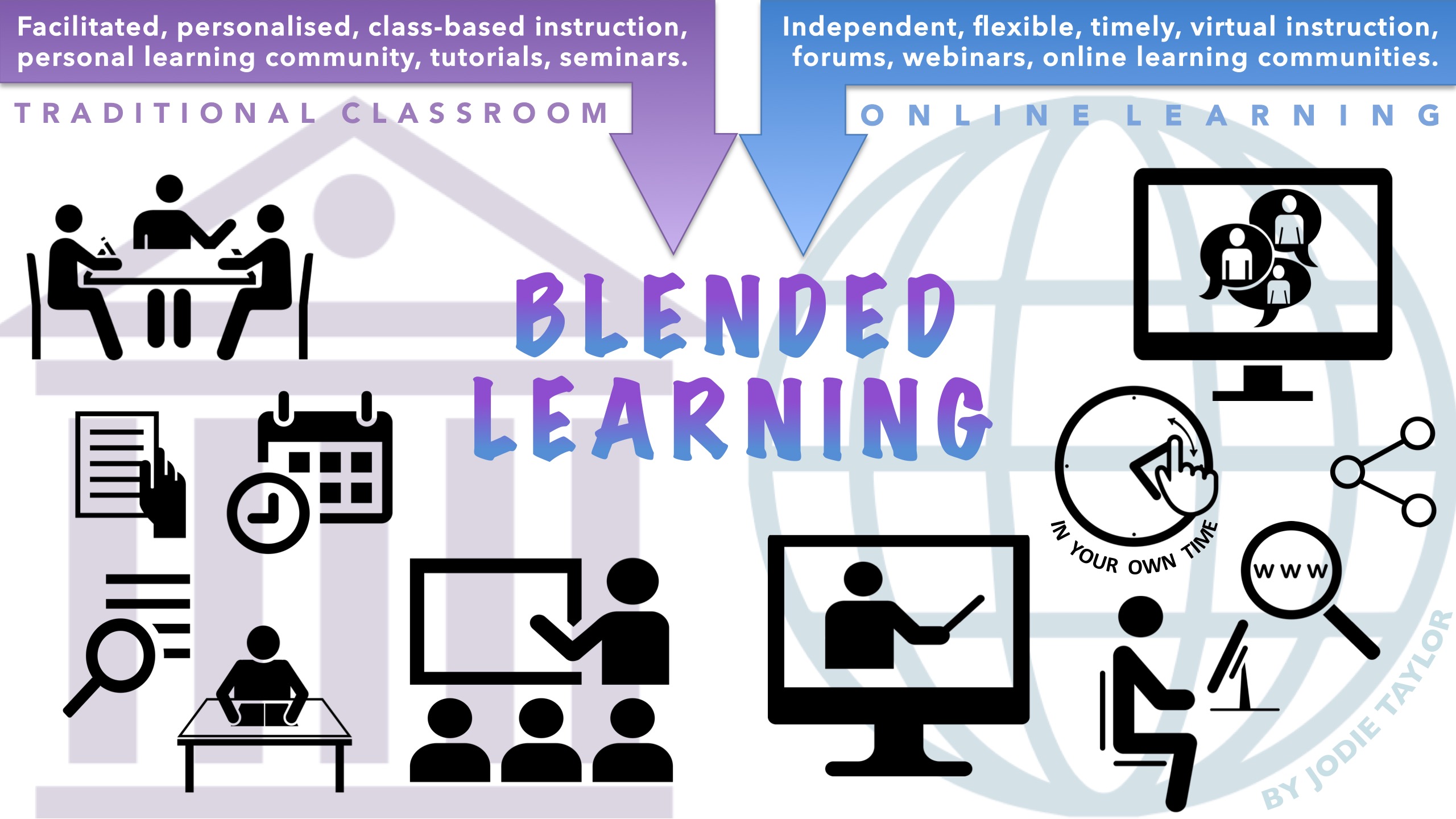
Blended learning has emerged as a powerful educational approach that combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online learning. This article explores the evolution of blended learning, its benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
What is Blended Learning?
Blended learning refers to an educational model that integrates in-person classroom experiences with online learning activities. This approach leverages digital tools and resources to enhance and complement traditional teaching methods. The goal is to create a more flexible and personalized learning experience for students.
The Historical Context
Blended learning has its roots in distance education, which began with correspondence courses and evolved into online learning platforms. The advent of digital technology and the internet has enabled the development of sophisticated online learning tools, making it possible to combine these tools with traditional classroom methods.
Key Models of Blended Learning
Several models of blended learning are commonly used in educational institutions:
Flipped Classroom: In this model, students learn new content online at home and then engage in interactive, hands-on activities in the classroom. This approach allows for more in-depth exploration of concepts during class time.
Rotation Model: Students rotate between online and face-to-face instruction in a structured schedule. This model can be implemented in various formats, such as station rotation, lab rotation, or individual rotation.
Flex Model: The flex model provides students with a high degree of flexibility, allowing them to learn primarily online with periodic in-person check-ins or support sessions. This model is particularly useful for personalized learning.
A La Carte Model: Students take some courses online while attending traditional classes for others. This model offers a mix of digital and in-person learning experiences based on student needs and preferences.
Benefits of Blended Learning
Blended learning offers several advantages for both students and educators:
Personalization: Digital tools enable educators to tailor learning experiences to individual student needs, providing personalized feedback and support.
Flexibility: Students can access online resources and complete assignments at their own pace, accommodating different learning styles and schedules.
Enhanced Engagement: Interactive digital content and multimedia resources can make learning more engaging and motivating for students.
Increased Access: Blended learning can provide access to high-quality educational resources and opportunities for students in remote or underserved areas.
Challenges and Considerations
While blended learning has many benefits, it also presents challenges:
Technology Integration: Ensuring that both students and educators have access to and are proficient in using digital tools can be a significant barrier.
Equity Issues: Not all students have equal access to technology and internet connectivity, which can create disparities in learning experiences.
Teacher Training: Educators need ongoing professional development to effectively design and implement blended learning strategies.
Balancing Online and In-Person Components: Finding the right balance between online and face-to-face instruction requires careful planning and consideration of course objectives.
The Future of Blended Learning
The future of blended learning is promising, with continued advancements in technology and educational practices. Innovations such as artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and adaptive learning platforms are likely to further enhance the effectiveness of blended learning models. As educational institutions increasingly adopt these approaches, blended learning will continue to evolve, offering new opportunities for personalized and engaging learning experiences.